LAWS
The three fundamental gas laws discover the relationship of pressure, temperature, volume and amount of gas. Boyle's Law tells us that the volume of gas increases as the pressure decreases. Charles' Law tells us that the volume of gas increases as the temperature increases. And Avogadro's Law tell us that the volume of gas increases as the amount of gas increases. The ideal gas law is the combination of the three simple gas laws.

Conservation Laws
Conservation of Energy
Energy can be neither created nor destroyed; the energy of the universe is constant. This is the First Law of Thermodynamics.
Conservation of Mass
Also known as Conservation of Matter. Matter can be neither created nor destroyed, though it can be rearranged. Mass remains constant in an ordinary chemical change.
GAS LAWS
Dalton's Law
The pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the component gases.
P V = n R T
predicts how the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas depend upon the number of moles of the gas. The number of moles, n, is the total moles of all the gas-phase species.
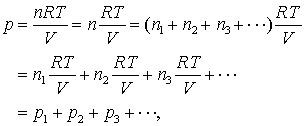

Gay-Lussac's Law

The ratio between the combining volumes of gases and the product (if gaseous) can be expressed in small whole numbers.
Pi/Ti = Pf/Tf
where
Pi = initial pressure
Ti = initial absolute temperature
Pf = final pressure
Tf = final absolute temperature